Draw a Circle on Canvas Html
Drawing shapes with canvas
- « Previous
- Next »
Now that we have set up our canvas environment, we can get into the details of how to draw on the canvas. By the cease of this article, you volition take learned how to draw rectangles, triangles, lines, arcs and curves, providing familiarity with some of the basic shapes. Working with paths is essential when drawing objects onto the canvas and we will see how that tin be done.
The grid
Earlier we can showtime drawing, we need to talk about the canvas grid or coordinate infinite. Our HTML skeleton from the previous folio had a canvas element 150 pixels wide and 150 pixels loftier.

Unremarkably 1 unit in the grid corresponds to 1 pixel on the canvas. The origin of this grid is positioned in the meridian left corner at coordinate (0,0). All elements are placed relative to this origin. Then the position of the top left corner of the blue square becomes 10 pixels from the left and y pixels from the elevation, at coordinate (ten,y). Later in this tutorial we'll meet how we can translate the origin to a different position, rotate the grid and even scale it, but for now we'll stick to the default.
Cartoon rectangles
Unlike SVG, <canvas> only supports two archaic shapes: rectangles and paths (lists of points continued past lines). All other shapes must exist created past combining i or more than paths. Luckily, we accept an array of path cartoon functions which get in possible to compose very circuitous shapes.
First let's look at the rectangle. There are three functions that draw rectangles on the canvass:
-
fillRect(x, y, width, height) -
Draws a filled rectangle.
-
strokeRect(ten, y, width, superlative) -
Draws a rectangular outline.
-
clearRect(x, y, width, height) -
Clears the specified rectangular area, making it fully transparent.
Each of these three functions takes the same parameters. x and y specify the position on the canvas (relative to the origin) of the top-left corner of the rectangle. width and height provide the rectangle's size.
Below is the draw() function from the previous page, but now it is making use of these iii functions.
Rectangular shape instance
function draw ( ) { var canvas = document. getElementById ( 'sail' ) ; if (sheet.getContext) { var ctx = sail. getContext ( '2d' ) ; ctx. fillRect ( 25 , 25 , 100 , 100 ) ; ctx. clearRect ( 45 , 45 , threescore , sixty ) ; ctx. strokeRect ( 50 , l , 50 , l ) ; } } This example'due south output is shown below.
The fillRect() function draws a large black foursquare 100 pixels on each side. The clearRect() part so erases a 60x60 pixel square from the eye, and then strokeRect() is called to create a rectangular outline 50x50 pixels within the cleared square.
In upcoming pages we'll meet two alternative methods for clearRect(), and we'll too see how to change the color and stroke mode of the rendered shapes.
Unlike the path functions we'll see in the next section, all three rectangle functions draw immediately to the canvas.
Drawing paths
Now allow'due south look at paths. A path is a listing of points, continued by segments of lines that can be of unlike shapes, curved or non, of different width and of different color. A path, or even a subpath, tin can be closed. To brand shapes using paths, we take some actress steps:
- Showtime, yous create the path.
- Then you use drawing commands to draw into the path.
- One time the path has been created, you can stroke or fill the path to render it.
Here are the functions used to perform these steps:
-
beginPath() -
Creates a new path. In one case created, future cartoon commands are directed into the path and used to build the path up.
- Path methods
-
Methods to gear up dissimilar paths for objects.
-
closePath() -
Adds a straight line to the path, going to the start of the current sub-path.
-
stroke() -
Draws the shape by stroking its outline.
-
fill() -
Draws a solid shape past filling the path's content area.
The first step to create a path is to call the beginPath(). Internally, paths are stored as a list of sub-paths (lines, arcs, etc) which together form a shape. Every time this method is chosen, the list is reset and we can start cartoon new shapes.
Notation: When the current path is empty, such as immediately after calling beginPath(), or on a newly created canvas, the first path construction command is always treated equally a moveTo(), regardless of what it actually is. For that reason, you will about always want to specifically fix your starting position after resetting a path.
The second pace is calling the methods that actually specify the paths to be drawn. Nosotros'll meet these shortly.
The 3rd, and an optional footstep, is to phone call closePath(). This method tries to shut the shape by drawing a directly line from the current indicate to the start. If the shape has already been closed or there's merely one point in the list, this part does nothing.
Annotation: When you call fill up(), any open shapes are closed automatically, so you don't take to call closePath(). This is not the example when you phone call stroke().
Drawing a triangle
For case, the code for drawing a triangle would look something like this:
function draw ( ) { var sheet = certificate. getElementById ( 'canvas' ) ; if (canvas.getContext) { var ctx = canvas. getContext ( '2d' ) ; ctx. beginPath ( ) ; ctx. moveTo ( 75 , 50 ) ; ctx. lineTo ( 100 , 75 ) ; ctx. lineTo ( 100 , 25 ) ; ctx. fill ( ) ; } } The result looks similar this:
Moving the pen
I very useful function, which doesn't actually draw anything but becomes role of the path list described above, is the moveTo() function. You can probably best remember of this as lifting a pen or pencil from 1 spot on a piece of paper and placing it on the next.
-
moveTo(x, y) -
Moves the pen to the coordinates specified by
xandy.
When the sail is initialized or beginPath() is called, you typically will want to use the moveTo() function to place the starting signal somewhere else. We could also apply moveTo() to draw unconnected paths. Take a expect at the smiley face below.
To try this for yourself, you can utilize the code snippet below. Just paste it into the draw() role nosotros saw earlier.
function describe ( ) { var canvas = certificate. getElementById ( 'sheet' ) ; if (canvas.getContext) { var ctx = canvas. getContext ( '2nd' ) ; ctx. beginPath ( ) ; ctx. arc ( 75 , 75 , 50 , 0 , Math. PI * ii , true ) ; // Outer circle ctx. moveTo ( 110 , 75 ) ; ctx. arc ( 75 , 75 , 35 , 0 , Math. PI , false ) ; // Mouth (clockwise) ctx. moveTo ( 65 , 65 ) ; ctx. arc ( threescore , 65 , five , 0 , Math. PI * 2 , truthful ) ; // Left centre ctx. moveTo ( 95 , 65 ) ; ctx. arc ( 90 , 65 , v , 0 , Math. PI * 2 , true ) ; // Correct centre ctx. stroke ( ) ; } } The result looks like this:
If y'all'd like to see the connecting lines, you can remove the lines that call moveTo().
Note: To learn more about the arc() function, run across the Arcs section beneath.
Lines
For drawing straight lines, use the lineTo() method.
-
lineTo(ten, y) -
Draws a line from the electric current drawing position to the position specified by
xandy.
This method takes 2 arguments, ten and y, which are the coordinates of the line's end betoken. The starting point is dependent on previously drawn paths, where the end signal of the previous path is the starting point for the following, etc. The starting point can besides be changed by using the moveTo() method.
The example below draws two triangles, one filled and one outlined.
part draw ( ) { var canvas = document. getElementById ( 'canvas' ) ; if (canvas.getContext) { var ctx = sail. getContext ( '2d' ) ; // Filled triangle ctx. beginPath ( ) ; ctx. moveTo ( 25 , 25 ) ; ctx. lineTo ( 105 , 25 ) ; ctx. lineTo ( 25 , 105 ) ; ctx. fill ( ) ; // Stroked triangle ctx. beginPath ( ) ; ctx. moveTo ( 125 , 125 ) ; ctx. lineTo ( 125 , 45 ) ; ctx. lineTo ( 45 , 125 ) ; ctx. closePath ( ) ; ctx. stroke ( ) ; } } This starts by calling beginPath() to start a new shape path. We so utilize the moveTo() method to move the starting point to the desired position. Below this, two lines are fatigued which make upward two sides of the triangle.
You'll observe the difference between the filled and stroked triangle. This is, as mentioned higher up, because shapes are automatically closed when a path is filled, but not when they are stroked. If we left out the closePath() for the stroked triangle, simply 2 lines would have been drawn, not a complete triangle.
Arcs
To draw arcs or circles, we apply the arc() or arcTo() methods.
-
arc(x, y, radius, startAngle, endAngle, counterclockwise) -
Draws an arc which is centered at (x, y) position with radius r starting at startAngle and ending at endAngle going in the given management indicated by counterclockwise (defaulting to clockwise).
-
arcTo(x1, y1, x2, y2, radius) -
Draws an arc with the given control points and radius, continued to the previous point by a straight line.
Let'southward have a more than detailed look at the arc method, which takes 6 parameters: ten and y are the coordinates of the center of the circle on which the arc should be drawn. radius is cocky-explanatory. The startAngle and endAngle parameters ascertain the start and end points of the arc in radians, along the bend of the circle. These are measured from the ten centrality. The counterclockwise parameter is a Boolean value which, when true, draws the arc counterclockwise; otherwise, the arc is drawn clockwise.
Annotation: Angles in the arc function are measured in radians, non degrees. To catechumen degrees to radians you can use the following JavaScript expression: radians = (Math.PI/180)*degrees.
The following example is a petty more complex than the ones we've seen above. It draws 12 different arcs all with different angles and fills.
The two for loops are for looping through the rows and columns of arcs. For each arc, we start a new path by calling beginPath(). In the code, each of the parameters for the arc is in a variable for clarity, but you wouldn't necessarily do that in existent life.
The ten and y coordinates should be articulate enough. radius and startAngle are fixed. The endAngle starts at 180 degrees (half a circle) in the first column and is increased by steps of 90 degrees, culminating in a consummate circle in the last cavalcade.
The statement for the clockwise parameter results in the outset and 3rd row existence drawn as clockwise arcs and the 2nd and fourth row as counterclockwise arcs. Finally, the if statement makes the top half stroked arcs and the bottom one-half filled arcs.
Note: This case requires a slightly larger canvas than the others on this page: 150 ten 200 pixels.
part draw ( ) { var sheet = document. getElementById ( 'canvas' ) ; if (canvas.getContext) { var ctx = canvass. getContext ( '2d' ) ; for ( var i = 0 ; i < 4 ; i++ ) { for ( var j = 0 ; j < iii ; j++ ) { ctx. beginPath ( ) ; var 10 = 25 + j * l ; // x coordinate var y = 25 + i * l ; // y coordinate var radius = 20 ; // Arc radius var startAngle = 0 ; // Starting bespeak on circle var endAngle = Math. PI + (Math. PI * j) / 2 ; // Cease indicate on circle var counterclockwise = i % 2 !== 0 ; // clockwise or counterclockwise ctx. arc (x, y, radius, startAngle, endAngle, counterclockwise) ; if (i > 1 ) { ctx. fill ( ) ; } else { ctx. stroke ( ) ; } } } } } Bezier and quadratic curves
The next blazon of paths bachelor are Bézier curves, bachelor in both cubic and quadratic varieties. These are mostly used to draw complex organic shapes.
-
quadraticCurveTo(cp1x, cp1y, x, y) -
Draws a quadratic Bézier bend from the current pen position to the end point specified past
tenandy, using the control point specified bycp1xandcp1y. -
bezierCurveTo(cp1x, cp1y, cp2x, cp2y, x, y) -
Draws a cubic Bézier curve from the current pen position to the finish signal specified by
xandy, using the control points specified by (cp1x,cp1y) and (cp2x, cp2y).
The difference between these is that a quadratic Bézier curve has a commencement and an end point (blue dots) and merely one control point (indicated by the red dot) while a cubic Bézier bend uses two control points. 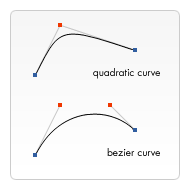
The 10 and y parameters in both of these methods are the coordinates of the terminate point. cp1x and cp1y are the coordinates of the first control signal, and cp2x and cp2y are the coordinates of the second control point.
Using quadratic and cubic Bézier curves can be quite challenging, because unlike vector drawing software like Adobe Illustrator, we don't have directly visual feedback as to what we're doing. This makes it pretty hard to draw complex shapes. In the post-obit example, nosotros'll be cartoon some unproblematic organic shapes, simply if y'all have the time and, most of all, the patience, much more than complex shapes can be created.
There's zip very difficult in these examples. In both cases we meet a succession of curves being fatigued which finally result in a complete shape.
Quadratic Bezier curves
This example uses multiple quadratic Bézier curves to render a speech balloon.
role draw ( ) { var canvas = document. getElementById ( 'sheet' ) ; if (sail.getContext) { var ctx = canvas. getContext ( '2d' ) ; // Quadratic curves example ctx. beginPath ( ) ; ctx. moveTo ( 75 , 25 ) ; ctx. quadraticCurveTo ( 25 , 25 , 25 , 62.5 ) ; ctx. quadraticCurveTo ( 25 , 100 , 50 , 100 ) ; ctx. quadraticCurveTo ( 50 , 120 , thirty , 125 ) ; ctx. quadraticCurveTo ( threescore , 120 , 65 , 100 ) ; ctx. quadraticCurveTo ( 125 , 100 , 125 , 62.five ) ; ctx. quadraticCurveTo ( 125 , 25 , 75 , 25 ) ; ctx. stroke ( ) ; } } Cubic Bezier curves
This example draws a centre using cubic Bézier curves.
function draw ( ) { var canvas = document. getElementById ( 'canvas' ) ; if (canvas.getContext) { var ctx = canvas. getContext ( '2d' ) ; // Cubic curves example ctx. beginPath ( ) ; ctx. moveTo ( 75 , 40 ) ; ctx. bezierCurveTo ( 75 , 37 , 70 , 25 , l , 25 ) ; ctx. bezierCurveTo ( twenty , 25 , 20 , 62.v , 20 , 62.v ) ; ctx. bezierCurveTo ( 20 , fourscore , 40 , 102 , 75 , 120 ) ; ctx. bezierCurveTo ( 110 , 102 , 130 , lxxx , 130 , 62.v ) ; ctx. bezierCurveTo ( 130 , 62.five , 130 , 25 , 100 , 25 ) ; ctx. bezierCurveTo ( 85 , 25 , 75 , 37 , 75 , 40 ) ; ctx. fill ( ) ; } } Rectangles
In addition to the iii methods we saw in Drawing rectangles, which draw rectangular shapes directly to the canvas, there's likewise the rect() method, which adds a rectangular path to a currently open path.
-
rect(x, y, width, height) -
Draws a rectangle whose top-left corner is specified by (
x,y) with the specifiedwidthandacme.
Before this method is executed, the moveTo() method is automatically called with the parameters (x,y). In other words, the current pen position is automatically reset to the default coordinates.
Making combinations
So far, each example on this folio has used just 1 blazon of path function per shape. All the same, in that location'southward no limitation to the number or types of paths y'all can use to create a shape. Then in this concluding example, allow'due south combine all of the path functions to make a set of very famous game characters.
function draw ( ) { var canvas = document. getElementById ( 'canvas' ) ; if (canvas.getContext) { var ctx = canvas. getContext ( '2d' ) ; roundedRect (ctx, 12 , 12 , 150 , 150 , 15 ) ; roundedRect (ctx, 19 , 19 , 150 , 150 , 9 ) ; roundedRect (ctx, 53 , 53 , 49 , 33 , 10 ) ; roundedRect (ctx, 53 , 119 , 49 , 16 , 6 ) ; roundedRect (ctx, 135 , 53 , 49 , 33 , x ) ; roundedRect (ctx, 135 , 119 , 25 , 49 , 10 ) ; ctx. beginPath ( ) ; ctx. arc ( 37 , 37 , 13 , Math. PI / 7 , -Math. PI / seven , false ) ; ctx. lineTo ( 31 , 37 ) ; ctx. fill ( ) ; for ( var i = 0 ; i < 8 ; i++ ) { ctx. fillRect ( 51 + i * 16 , 35 , four , 4 ) ; } for (i = 0 ; i < 6 ; i++ ) { ctx. fillRect ( 115 , 51 + i * 16 , iv , 4 ) ; } for (i = 0 ; i < 8 ; i++ ) { ctx. fillRect ( 51 + i * xvi , 99 , 4 , 4 ) ; } ctx. beginPath ( ) ; ctx. moveTo ( 83 , 116 ) ; ctx. lineTo ( 83 , 102 ) ; ctx. bezierCurveTo ( 83 , 94 , 89 , 88 , 97 , 88 ) ; ctx. bezierCurveTo ( 105 , 88 , 111 , 94 , 111 , 102 ) ; ctx. lineTo ( 111 , 116 ) ; ctx. lineTo ( 106.333 , 111.333 ) ; ctx. lineTo ( 101.666 , 116 ) ; ctx. lineTo ( 97 , 111.333 ) ; ctx. lineTo ( 92.333 , 116 ) ; ctx. lineTo ( 87.666 , 111.333 ) ; ctx. lineTo ( 83 , 116 ) ; ctx. fill ( ) ; ctx.fillStyle = 'white' ; ctx. beginPath ( ) ; ctx. moveTo ( 91 , 96 ) ; ctx. bezierCurveTo ( 88 , 96 , 87 , 99 , 87 , 101 ) ; ctx. bezierCurveTo ( 87 , 103 , 88 , 106 , 91 , 106 ) ; ctx. bezierCurveTo ( 94 , 106 , 95 , 103 , 95 , 101 ) ; ctx. bezierCurveTo ( 95 , 99 , 94 , 96 , 91 , 96 ) ; ctx. moveTo ( 103 , 96 ) ; ctx. bezierCurveTo ( 100 , 96 , 99 , 99 , 99 , 101 ) ; ctx. bezierCurveTo ( 99 , 103 , 100 , 106 , 103 , 106 ) ; ctx. bezierCurveTo ( 106 , 106 , 107 , 103 , 107 , 101 ) ; ctx. bezierCurveTo ( 107 , 99 , 106 , 96 , 103 , 96 ) ; ctx. fill ( ) ; ctx.fillStyle = 'blackness' ; ctx. beginPath ( ) ; ctx. arc ( 101 , 102 , 2 , 0 , Math. PI * 2 , true ) ; ctx. fill ( ) ; ctx. beginPath ( ) ; ctx. arc ( 89 , 102 , 2 , 0 , Math. PI * 2 , true ) ; ctx. fill ( ) ; } } // A utility role to depict a rectangle with rounded corners. part roundedRect ( ctx, x, y, width, meridian, radius ) { ctx. beginPath ( ) ; ctx. moveTo (x, y + radius) ; ctx. arcTo (x, y + summit, x + radius, y + top, radius) ; ctx. arcTo (x + width, y + height, x + width, y + height - radius, radius) ; ctx. arcTo (x + width, y, ten + width - radius, y, radius) ; ctx. arcTo (x, y, x, y + radius, radius) ; ctx. stroke ( ) ; } The resulting image looks like this:
We won't go over this in detail, since it's really surprisingly unproblematic. The most important things to note are the use of the fillStyle property on the drawing context, and the utilise of a utility role (in this case roundedRect()). Using utility functions for bits of drawing yous practise oftentimes can be very helpful and reduce the corporeality of code you need, too equally its complexity.
Nosotros'll take another await at fillStyle, in more detail, later in this tutorial. Here, all nosotros're doing is using it to change the fill colour for paths from the default colour of blackness to white, and and so back again.
Path2D objects
Equally we have seen in the final instance, there can be a series of paths and drawing commands to describe objects onto your canvas. To simplify the lawmaking and to improve performance, the Path2D object, available in recent versions of browsers, lets you enshroud or record these drawing commands. Y'all are able to play back your paths apace. Let's meet how we can construct a Path2D object:
-
Path2D() -
The
Path2D()constructor returns a newly instantiatedPath2Dobject, optionally with some other path as an argument (creates a copy), or optionally with a cord consisting of SVG path data.
new Path2D ( ) ; // empty path object new Path2D (path) ; // copy from another Path2D object new Path2D (d) ; // path from SVG path data All path methods like moveTo, rect, arc or quadraticCurveTo, etc., which we got to know in a higher place, are available on Path2D objects.
The Path2D API also adds a way to combine paths using the addPath method. This tin can exist useful when you desire to build objects from several components, for example.
-
Path2D.addPath(path [, transform]) -
Adds a path to the current path with an optional transformation matrix.
Path2D example
In this example, nosotros are creating a rectangle and a circle. Both are stored equally a Path2D object, and then that they are available for subsequently usage. With the new Path2D API, several methods got updated to optionally have a Path2D object to use instead of the electric current path. Here, stroke and fill are used with a path statement to draw both objects onto the sheet, for example.
office draw ( ) { var sail = document. getElementById ( 'sheet' ) ; if (canvas.getContext) { var ctx = canvas. getContext ( '2d' ) ; var rectangle = new Path2D ( ) ; rectangle. rect ( 10 , 10 , 50 , l ) ; var circumvolve = new Path2D ( ) ; circle. arc ( 100 , 35 , 25 , 0 , two * Math. PI ) ; ctx. stroke (rectangle) ; ctx. fill up (circle) ; } } Using SVG paths
Another powerful feature of the new canvas Path2D API is using SVG path information to initialize paths on your canvas. This might allow you to pass around path data and re-use them in both, SVG and canvas.
The path volition move to indicate (M10 10) and and so motion horizontally 80 points to the right (h 80), and then fourscore points down (v fourscore), then 80 points to the left (h -80), and so back to the start (z). You can see this example on the Path2D constructor page.
var p = new Path2D ( 'M10 x h eighty v 80 h -80 Z' ) ; - « Previous
- Next »
Source: https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/Canvas_API/Tutorial/Drawing_shapes
0 Response to "Draw a Circle on Canvas Html"
Post a Comment